Study Finds Medicinal Plants Consumed by Gorillas Have Antibacterial and Antioxidant Properties.
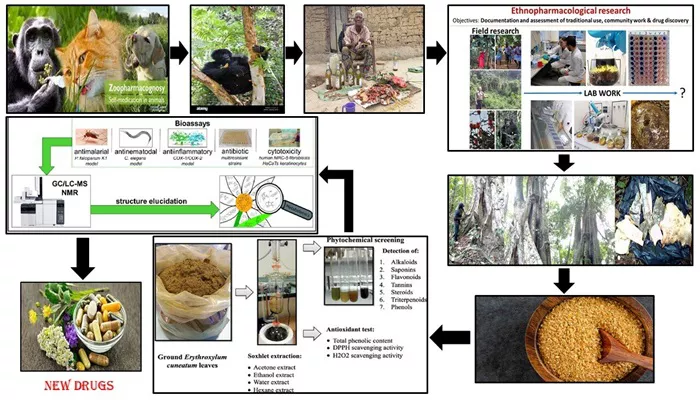
A new study published on September 11 in PLOS ONE reveals that four plants, eaten by wild gorillas in Gabon and used in local traditional medicine, possess significant antibacterial and antioxidant properties. The research, led by Leresche Even Doneilly Oyaba Yinda from the Interdisciplinary Medical Research Center of Franceville, sheds light on these plants’ potential medicinal benefits.
Wild gorillas are known to consume various plants that help them treat ailments, and local communities often use these same plants in traditional medicine. To explore this connection, researchers observed western lowland gorillas (Gorilla gorilla gorilla) in Moukalaba-Doudou National Park, documenting their plant consumption. They then interviewed 27 residents of the nearby village of Doussala, including traditional healers and herbalists, about their use of these plants.
The study identified four plant species that are both consumed by gorillas and utilized in local medicine: the fromager tree (Ceiba pentandra), giant yellow mulberry (Myrianthus arboreus), African teak (Milicia excelsa), and fig trees (Ficus). Bark samples from these plants were tested for antibacterial and antioxidant properties, as well as their chemical composition.
The results showed that all four plants’ bark had antibacterial activity against at least one multidrug-resistant strain of Escherichia coli, with the fromager tree displaying the most notable effectiveness. Each plant contained compounds with medicinal properties, such as phenols, alkaloids, flavonoids, and proanthocyanidins. However, it remains unclear whether gorillas consume these plants for medicinal reasons or other purposes.
Central Africa’s rich biodiversity offers a vast array of potentially medicinal plants. This study provides initial insights into the antibacterial and antimicrobial potential of these four plants, suggesting they could be valuable targets for future drug discovery, especially for combating multidrug-resistant bacterial infections.
The researchers emphasize that alternative medicines and therapies are promising for addressing current and future public health challenges. They highlight zoopharmacognosy, the study of how animals use plants for medicinal purposes, as a promising approach for discovering new drugs.