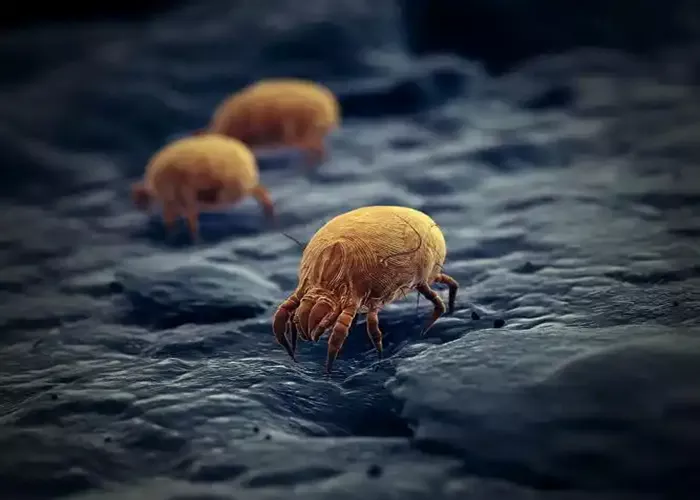
Mites, these extremely tiny creatures, quietly threaten the health and vitality of plants. In the microscopic world of plants, mites are inconspicuous, but they can reproduce at an alarming rate, causing serious harm to plants. They Pierce plant cells and suck sap, causing the leaves to appear mottled, yellow, curled and other symptoms, and even lead to impeded plant growth, wilt and death in severe cases.
Whether it is the delicate flowers in the indoor pot, or the lush green plants in the outdoor garden, it can become the target of mites. Therefore, in-depth understanding of the characteristics and hazards of mites, and mastering effective prevention and control methods are crucial for every person who loves plants. This is not only necessary to protect plants from harm, but also the key to creating a green, healthy plant environment.
The Characteristics And Hazards Of Mites
Mites belong to arachnoid Acariformes, small in size, mostly 0.1-1mm, need to be observed with the help of a microscope. Its body is oval or round, with four pairs of legs. Leaf mites and red spiders are mainly closely related to plants. Leaf mites often live on the back of leaves, piercing plant cells with their mouthparts to suck up juice. At first, the affected leaves appeared green spots of pinpoint size, and then gradually expanded and fused to form yellow or brown spots. In severe cases, the leaves became dry and curled off, affecting photosynthesis and plant growth. Red spiders multiply quickly in hot and dry conditions and form webs on plant leaves, impeding gas exchange and water transpiration. The leaves of the plants affected by it lose luster, are grayish white or yellowish white, the growth potential is weak, the flowers and fruits are stunted, and the whole plant dies when it is serious. Mites have strong reproductive ability, and under suitable conditions, female mites can lay dozens to hundreds of eggs in their lifetime, and the young mites can develop into adult mites in a short time after hatching. And mites have strong transmission, can be spread by wind, insects, human activities and plant material transportation, easy to cause large-scale plant diseases and pests.
Comprehensive Measures To Prevent Mite Infesting
1. Environmental control: Create a space that is not suitable for mites
Temperature and humidity management
Mites are sensitive to temperature and humidity. Maintaining relative humidity of 40%-60% can inhibit its growth and reproduction. Such as dry winter with humidifier humidification, summer high temperature and rainy ventilation to reduce humidity. Controlling the ambient temperature at 20-25 ° C can reduce the breeding of mites.
Light regulation
Reasonable light is important to plants and affects the survival of mites. Heliotropic plants in full sun but suitable shade in summer; Shade-loving plants are placed in a bright scattering light environment. Good light helps plants grow healthily and enhances their resistance to mites.
2. Plant selection and layout: Construct anti-mite plant defense line
Select mite resistant plant varieties
When planting, preference should be given to varieties with natural mite resistance. Such as mint, lavender and other vanilla plant odor repellent mites; Geranium and marigold contain anti-mite substances.
Rational arrangement of plants
It is arranged according to plant habit and mite resistance. Avoid concentrated planting of mite prone plants, and plant mite resistant and susceptible plants in space. Such as roses and rosemary in the garden staggered planting, reduce the risk of mite spread, create a beautiful ecological balance landscape.
3. Daily maintenance and management: strengthen the foundation of plant health
Cleaning and trimming
Clean plants regularly, remove fallen leaves, flowers, weeds, and reduce the hiding places of mites. Potted plants can be moved outside to rinse the leaves. Timely trim over dense branches and leaves, dead branches, improve ventilation and light conditions. Such as pruning fruit trees in spring, thinning cross branches, etc., to prevent the breeding of leaf mites.
Fertilization and watering
Reasonable fertilization can provide adequate nutrients for plants and enhance their stress resistance. According to the principle of “thin fertilizer and frequent application”, the appropriate fertilizer and amount are selected according to the growth stage of plants. If the growth peak period appropriate application of nitrogen fertilizer, before and after the flowering period to increase the application of phosphate potassium fertilizer. Scientific watering, keep the soil moderately moist without water. Succulents are “dry and watered.” Moisture-loving plants such as green plants keep the soil moist but their roots waterlogged.
Physical Mite Removal Methods And Their Applications
1. Water flushing method: a simple and efficient means of mite removal
Water flushing is effective for small potted plants. Put the pot in the sink or outdoor open place at an Angle, wash the front and back of the leaves, the stalk and stem with strong water flow of the watering can or water pipe, and wash away the mites and their eggs. If the potted rose infected with leaf mites is flushed once a week, the number of leaf mites can be greatly reduced by flushing 3-4 times. Control the intensity of water flow during operation to prevent plant damage, and release the ventilated place to dry the leaves quickly after flushing to prevent diseases caused by excessive humidity. For delicate or water-sensitive plants, reduce the intensity or frequency of precipitation flow, or blot the leaves with paper towels after rinsing.
2. Wiping method: precise removal of mites
The wiping method is suitable for plants with few, thick or fuzzy leaves. With a soft wet cloth or sponge dipped in water or mild soapy water, gently wipe the leaf surface to remove mites and their secretions, eggs, etc. Such as succulent plant leaf gap mites, the effect of this method is good. Wipe gently to avoid damaging the leaves, and then keep ventilation to let the leaves dry naturally.
3. Isolation method: prevent the spread of mites
If individual plants are found to be infested with mites, isolate them immediately and place them more than 1-2 meters apart from healthy plants. Plants with severe mite infestation were placed in a separate room or area and removed without signs of recurrence. For example, in greenhouse flowers, a pot of flowers contaminated with leaf mites should be moved to the quarantine area, and the surrounding plants should be checked for prevention and prevention of the spread of leaf mites.
The Strategy And Practice Of Biological Control Of Mites
1. The application of predatory mites: the ecological wisdom of treating mites with mites
Predator mites are natural enemies of mites, such as Phytoseius chilensis, Amblyseius gourami and so on. They reproduce quickly, eat strongly, and are adaptable. When feeding mites, the dosage and time should be determined according to plant species, number of mites and environmental conditions. It is better to throw 1000-5000 head per square meter of plant leaves, and put in the early stage of mite damage. For example, orchard prevention of leaf mites, when the initial movement of leaf mites did not explode in spring, the effect of 20,000-30,000 Chilean small phytoseiius mites per mu is good. Create a suitable environment for its survival, humidity 60%-80%, leave weeds or nectar plants, avoid broad-spectrum pesticides.
2. Utilization of beneficial insects: Building a multi-component biological control system
Beneficial insects such as lacewings and ladybugs larvae and adults eat mites, aphids and other pests. The larva of lacefly “aphid lion” has a surprising appetite, and the ladybug has a strong predation on leaf mites. Planting canola flowers, purple cloud and other honey plants to attract beneficial insects to roost and breed, insect hotels to provide shelter for them. Such as garden insect hotel, lead lacewings, ladybugs and so on stay, strong biological control effect on mites.
Key Points And Precautions Of Chemical Control Of Mites
1. Selection of acaricides: precise combat against mites
When selecting acaricides, select those that are specific to mites and safe for plants, people and the environment. Such as avermectin, acarine, spirodex and so on. Avermectin biogenic acaricide, good touch to kill stomach poison, short residue, environmentally friendly; Acarine has strong quick effect and long lasting effect; Spirogenin is a new type of acaricide, which inhibits the synthesis of lipid of mites, and is effective against all stages of mites with low resistance. The type and dosage of acaricide were selected according to mite species, occurrence degree and plant sensitivity. Abamectin spray was used for the initial onset of leaf mites. When the mite damage is heavy and there is resistance, the compound preparation of spiroxide and chlorazine is used.
2. Safe use of acaricides: protection of plants and human settlements
Use acaricide in strict accordance with the manual dose, concentration, method operation. Do not increase the amount or increase at will, to prevent drug damage and residue exceed the standard. A measuring instrument for the preparation of pharmaceutical products, keeping the concentration uniform. Spray evenly and thoughtfully, avoid high temperature and strong light period. If it is not sprayed at noon in summer, 9-11 am or 4-6 PM is appropriate. Dispose of the remaining chemicals and packaging properly after use, and observe the safety interval. Such as avermectin to treat vegetable mites, the safe interval is 7-14 days, during which the edible part of vegetables is not picked.
In the control of mites, prevention should be put in the first place, through environmental regulation, plant selection layout, daily maintenance to build a line of defense, combined with physical, biological and chemical control methods, according to the situation of mites and plant needs to determine comprehensive control strategies, protect plant vitality, so that plants and humans coexist in harmony.
Conclusion
In this silent battle with mites, we use science as a sword and patience as a shield, and we have cast a strong protective fortress for plants. Preventive measures, like a cornerstone, lay the foundation for the healthy growth of plants; Physical mite removal is like a pioneer, which directly weakens the force of mites; Biological control is still the backbone, with the force of nature to balance the mite population cleverly; Chemical control is backed up by precise strikes at critical moments.
However, mite control is not once and for all, but a lasting battle of protection. We need to stay alert at all times, regularly inspect the plant status, keenly detect the clues of mites, and timely adjust the control strategy to ensure that every plant can thrive under careful care and bloom their brilliant brilliance. Let us work together, with unremitting efforts and wisdom, in the long journey of plant maintenance, always guard this piece of green pure land, so that the full vitality of the plant world becomes a beautiful picture of our life that will never fade, and add a strong ink to the harmonious coexistence of nature.